SYNERGIA meets SDTaP’s IAC
By Theo Spyridopoulos: On the 15th of July, the Industrial Advisory Committee of the Security of Digital Technology at the Periphery (SDTaP) programme met, to hear updates from the three Demonstrator projects in Round 1:
- i-TRACE: IoT Transport Assured for Critical Environments, a collaboration between the University of Warwick, Cisco, BT, Senseon, and Costain working with Artificial Intelliegence and Distributed Ledger technologies.
- Secure-CAVs: The world’s first on-chip and in-life monitoring solution to rapidly detect cyber security threats in Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs), a collaboration between the Coventry, Southampton, Siemens, and Copper Horse.
- ManySecured: Collaborative development of Secure IoT Gateways & Routers, a collaboration between Cisco, NquiringMinds, the University of Oxford, and our friends at the IoT Security Foundation.
and from Round 2:
- SYNERGIA: Secure bY desigN End to end platfoRm for larGe scale resource constrained Iot Applications, a collaboration between Toshiba’s Bristol R&D Lab, Configured Things, Ioetec, MAC Ltd, and Smartia.
In addition, we heard from two projects, led by PETRAS researchers, funded under SDTaP’s commercialisation stream through CyberASAP (Cyber Security Academic Startup Accelerator Programme), the only accelerator programme in the cybersecurity ecosystem for pre-seed funding:
- TAIMAS: Timing Anomalies as an Indicator of Mal-Intervention in Automation Systems (UCL and CUBE 2 Ltd in Worthing)
- THuVA: Improving Security with Techno-Human Vulnerability Analysis (UCL)
SYNERGIA falls under Theme 2 “Secure and energy-efficient IoT systems in resource-constrained environments” of InnovateUK’s “Demonstrators addressing cyber security challenges in the Internet of Things” round 2 call and focuses on end-to-end cyber security for IoT systems with resource-constrained devices. It involves Involves AI as part of the security detection and mitigation mechanism at the Edge and plans to demonstrate the results in a real environment based on an existing Edge IoT platform. Similar challenges and areas of interest, especially in the field of AI at the Edge Gateway and Secure Configuration Management of thousands of IoT devices at the Edge, were also identified during the meeting. Project TAIMAS in particular, uses autoencoders for anomaly detection to perform intrusion detection in Building Automation Systems in a similar way to us. In SYNERGIA we push the detection to the Edge providing a human-in-the-loop under a Federated Learning Architecture to improve the model’s performance in case of low confidence outputs.
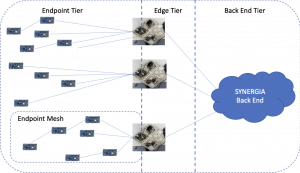
SYNERGIA focuses on a secure-by-design end-to-end platform for large scale resource-constrained IoT applications. We follow a three-tier architecture that includes i) the resource-constrained Endpoint Tier where battery-powered sensor devices are scattered in the field, ii) the Edge Tier that is geographically located close to the Endpoints and is responsible for collecting the sensor data and provide processing capabilities used for data analytics and system configuration management at the Edge and iii) the Back End Tier that is responsible for aggregating the processed data from the Edge Tier and providing a User Interface to End-users.
To inform the design of our security solutions, we conducted a threat analysis for the whole end-to-end system based on NIST’s threat modelling process in the 800-30 special publication. The main threats we are interested in revolve around unauthorised/malevolent users, services and devices trying to access or disrupt our system, targeting the Endpoint and Edge Tiers. To address these threats, we develop a series of security solutions operating at the two Tiers.
Similarly to the TAIMAS project, SYNERGIA uses an autoencoder running at the Edge to model the Edge device’s normal behaviour and detect abnormal behaviours. To improve the model’s performance, we use a human-in-the-loop approach under a Federated Learning architecture, providing a user interface for security experts to extract system data corresponding to low confidence model inferences for external analysis and data labelling. We also employ AI deployed at the Edge to detect malicious drifts in the data collected from the Endpoint devices.
A point raised during the meeting was the challenge of configuring and managing thousands of Endpoint devices scattered in the field; Intel has faced this issue with IoT deployments in the US. The existence of multiple actors and devices with different roles and owners respectively requires dynamic configuration management and control of the IoT. Providing this closer to the Endpoint Tier improves scalability as well as security and user privacy. In SYNERGIA, we address this challenge by delivering secure configuration and management of Endpoints, as well as secure Endpoint data processing through signed data flows deployed at the Edge.
SYNERGIA security is targeted at multiple resource constrained IoT for Smart Cities applications, and will demonstrate the solutions developed in just one particular Use Case: securing “Multi-tenancy Smart Buildings”. Working with Oxford Innovation (https://oxin.co.uk/), a number of Edge nodes and Endpoint sensors will be installed in the Future Space multi-tenancy building http://www.futurespacebristol.co.uk providing environmental monitoring, weather monitoring, green energy, and access control services etc. Synergia’s solutions will allow the building operator to deploy solutions around Variable billing based on room utilisation, heating, cooling etc. and also allow users a “Bring your own IoT device” policy. Furthermore, it will enable space users to ensure compliance with investors’ Environmental, Social and Corporate Governance policies.